So farewell, then, Trussonomics.
The demise of the country’s second shortest-lived chancellor also brings with it the demise of the country’s shortest-lived economic movement.
Liz Truss came into office promising to boost the country’s growth rate through a forensic combination of tax cuts, reforms to the country’s supply side (for which read: things like planning reform) and spending restraint. This was, if you squint a little bit, not dissimilar to the kinds of policies espoused by Ronald Reagan and Margaret Thatcher.
Tory MPs turn on Truss as PM scrambles to save job after sacking chancellor – latest updates
It always looked risky – especially at such a fragile point for the global economy. We are coming to the end of a 12-year period of cheap money, something which is causing a near-nervous breakdown in financial markets. Central banks are in the process of raising interest rates and trying to feed the glut of bonds they bought during the financial crisis back in the market.
As if that weren’t enough, Europe is facing one of its bleakest economic winters in modern memory, with a war raging in Ukraine and energy prices touching historic highs. It is hard to think of many less auspicious periods to attempt an untested new economic manifesto.
Yet Ms Truss and her former chancellor Kwasi Kwarteng pushed on all the same. And unlike Thatcher, whose first few budgets were grisly austerity packages which no one much enjoyed, Ms Truss and Mr Kwarteng aimed to turn Thatcherism on its head. Instead of fixing the public finances first and then cutting taxes second, they opted to spend the fruits of economic growth before that growth had even been achieved.
The mini-budget of 23 September was a small document with extraordinarily large consequences. Ironically, the more expensive the measures were, the less controversial they turned out to be. The scheme to cap household energy unit costs will potentially cost hundreds of billions of pounds, yet (and we know this because it was pre-announced long before the mini-budget) investors barely batted an eyelid. They carried on lending to this country at more or less the same or equivalent rates.
The same was not the case for the rest of the mini-budget’s policies. Shortly after they were announced – everything from the abolition of the 45p rate (actually quite cheap in fiscal terms) to the cancellation of Rishi Sunak’s corporation tax rise – markets began to lurch in what was, for Ms Truss, and most UK households, the wrong direction. The pound sank, the yields on government debt, which determine the interest rates across most of the economy, began to climb.
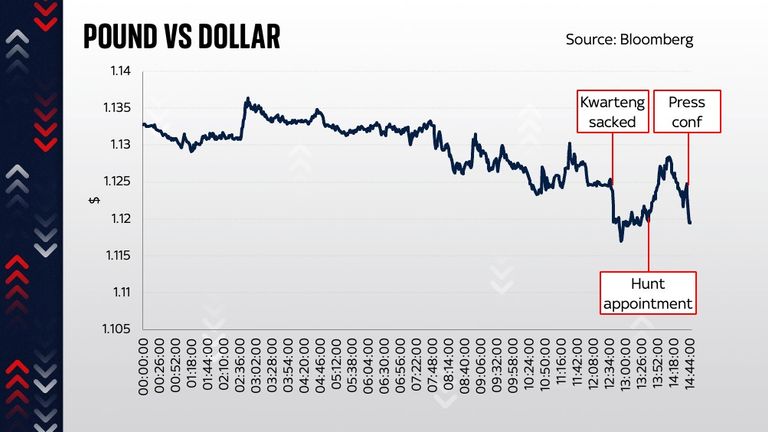
That was bad enough. When Mr Kwarteng announced gleefully a couple of days later on television that he had more tax cuts up his sleeve, the trot out of the country became a stampede. The pound fell, briefly, to the lowest level against the dollar in the history of, well, the dollar.
Even more worryingly, those interest rates on government bonds rose at an unprecedented rate, causing all sorts of malfunctions throughout the money markets.
The most obvious – and the one that perhaps will have the longest legacy – is the rise in mortgage rates. But the unexpected consequences were even more worrying, among them a crisis in funds used by pension schemes. That sparked a “run dynamic” which compelled the Bank of England to step in with an emergency support scheme.
Even at this point, we were into unprecedented territory. Never before had the Bank been forced to intervene quite like this. Never before had it had to do so as a result of a government’s Budget.
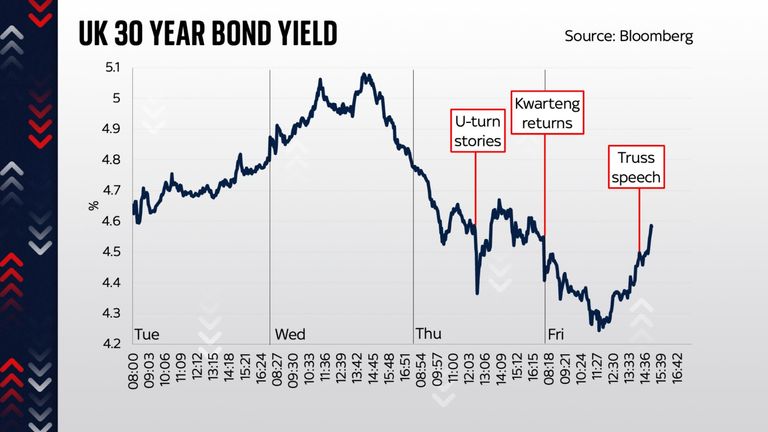
The intervention, however, had some success, bringing down the relevant interest rates and bringing markets back from the edge. But there was a sting in the tail: a deadline. Today, 14 October.
In hindsight perhaps it’s obvious that this, then, would always have been the day when the government might face another existential crisis. Investors were always going to be nervous ahead of the Bank’s withdrawal from this neck of the bond market. And that is precisely what happened: after the governor reiterated, on a panel in Washington, that he was indeed serious, all eyes then turned to the chancellor. Could he say something to reassure markets?
In the event, the answer was: no. But something else changed matters: growing rumours of a U-turn. That brings us to this morning. The chancellor, pulled back from Washington early, was dismissed. The U-turn began. The corporation tax freeze is to be abandoned. The coming medium-term fiscal plan will involve austerity and a big dose of fiscal pain. The upshot is that Trussonomics, which was hinged clearly on tax cuts like these, is dead in the water.
However, the bigger question concerns what happens next. Those markets, which Ms Truss said explicitly were the reason for her U-turn, are still pretty frantic. No one knows how they’ll fare on Monday, but, whether right or wrong, another grisly day will almost certainly be seen as a sign of the government’s failure. And, having sealed the fate of her chancellor, the markets could well seal the fate of the prime minister.
But that’s a few days away – a long time in both politics and markets.
In the meantime, here is something to dwell on: an alternative version of history. In a parallel universe, Ms Truss and Mr Kwarteng did things slightly less hastily. They decided their emergency Budget would simply deal with the energy price shock coming this winter. They promised an OBR statement and hatched plans for a growth-generating budget in a few months’ time.
In that parallel universe, interest rates probably wouldn’t have risen so high. The rises would, anyway, have been blamed on the Bank of England, not the government. The government would have enjoyed some kudos for having prevented energy-related penury this winter and made merry in their honeymoon. Things could have been oh-so different.
Click to subscribe to the Sky News Daily wherever you get your podcasts
Now, all of this is of course imponderable. But it does rather underline an important point: none of this was inevitable. This wasn’t a crisis like 1992 – where the UK faced monetary pressures suffered by nearly every other nation in Europe. It was simply a succession of very unfortunate decisions at precisely the wrong moment.
At a time of market turmoil and war in Europe, Ms Truss and Mr Kwarteng chose to take a gamble. It did not pay off.
To register your interest and share your story, please email TheGreatDebate@sky.uk